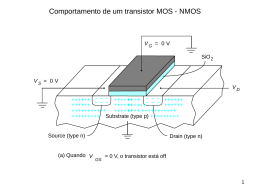
Concepção de Circuitos Integrados Projeto de Célula Projeto de uma Célula CMOS • Porta lógica: NAND de 2 entradas • Layout da porta NAND2 na tecnologia 0,8 m da AMS na ferramenta L-Edit do sistema Tanner. • Simulação da porta NAND2 na ferramenta HSPICE ou no simulador do Tanner: – Atraso da porta NAND2: tempo de subida (tr), tempo de descida (tf), atraso de subida (tdr) e atraso de descida (tdf) em relação ao tamanho dos transistores (W/L) e a carga da saída CL. – Potência da porta NAND2: em relação ao tamanho dos transistores (W/L), a carga de saída CL e a inclinação da tensão de entrada. Projeto de uma Célula CMOS Layout de uma NAND2 VDD A B S A B L = 0,8 m Wp = 2,0 m Wn = 2,0 m Projeto de uma Célula CMOS Layout de uma NAND2 - 2ª versão VDD A B S A B L = 0,8 m Wp = 2,0 m Wn = 2,0 m Projeto de uma Célula CMOS Layout de uma NAND2 - 3ª versão VDD A B S A B L = 0,8 m Wp = 6,0 m Wn = 4,0 m Projeto de uma Célula CMOS Atraso de uma porta NAND2 CL tr k 0.2 pVDD tf k CL n VDD 2 1 L R ( ) Cox (Vgs Vt ) W tdr Rp1CL tdf ( Rn1Cab ) [(Rn1 Rn 2 )CL ] VDD A A B tdf tdr tf tr B Rp1 Rn2 Rn1 CL Cab Atraso em relação a CL NAND2 com L= 0,8 m e Wn=Wp= 4 m CL= 0fF CL= 50fF CL= 0fF CL= 10fF CL= 20fF CL= 50fF Carga (CL) CL= 20fF Atraso da porta CL= 10fF Atraso em relação a W/L W=4 m W=6 m W=8 m W=2 m W=4 m W=6 m W=8 m Atraso da porta W=2 m Largura (W) do canal do transistor Carga CL = 10 fF, aproximadamente um fan-out = 5. Transistores com L= 0,8 m e Wn=Wp Atraso com Wp > Wn Carga CL = 10 fF, aproximadamente um fan-out = 5. Transistores com L= 0,8 m. Wp = 3 Wn Wp = 1,5 Wn Wp = 2 Wn Wp = 3 Wn Wp = 1,5 Wn Wp = 2 Wn Potência em relação a CL NAND2 com L= 0,8 m e Wn=Wp= 4 m potência potência potência 4 3 2 1 0 CL = 0 fF CL = 10 fF CL = 20 fF carga CL = 50 fF Potência em relação a W/L Carga CL = 10 fF, aproximadamente um fan-out = 5. Transistores com L= 0,8 m. potência potência potência 5 4 3 2 1 0 Wn=Wp=2 Wn=Wp=4 Wn=Wp=6 Wn=Wp=8 Largura do canal do transistor Power Dissipation in CMOS Circuits • There are two components: • Static Dissipation (PS) due to leakage current • Dynamic Dissipation (PD) due to: » Switching transient current; » Charging and discharging of load capacitances. Power Dissipation in CMOS Circuits • Static Dissipation: • Model describing parasitic diodes: Power Dissipation in CMOS Circuits • Static Dissipation: • The leakage current is described by the diode equation: Power Dissipation in CMOS Circuits • Static Dissipation: Power Dissipation in CMOS Circuits • Dynamic Dissipation: VDD A B Ic A B Icc CL Power Dissipation in CMOS Circuits • Dynamic Dissipation: Simulação no HSPICE Exemplo: nand2.sim (arquivo extraído do layout no L-Edit) C1 vdd gnd 3.29875FF C2 out gnd 0.91925FF C3 B gnd 1.3008FF C4 A gnd 1.3008FF C5 gnd gnd 2.87675FF Comandos para a utilização da ferramenta: xhost + rlogin sercial setenv DISPLAY <maquina>:0.0 hspice <arquivo.cir> >! <arquivo.out> gsi Capacitâncias extraídas M1 out B vdd vdd PMOS L=0.8U W=6U AD=6.9P PD=8.30U AS=13.5P PS=16.50U M2 vdd A out vdd PMOS L=0.8U W=6U AD=13.5P PD=16.50U AS=6.9P PS=8.30U M3 14 B out gnd NMOS L=0.8U W=4U AD=4.6P PD=6.30U AS=9P PS=12.50U M4 gnd A 14 gnd NMOS L=0.8U W=4U AD=9P PD=12.50U AS=4.6P PS=6.30U Simulação no HSPICE Exemplo: nand2.cir (arquivo extraído do layout no L-Edit) * CIRCUIT cellbasic .include ams.lib * Excitação do circuito V0 vdd gnd dc 5 V1 A gnd PULSE(0 5 0N 0.6N 0.6N 25N 50N) * (Vinicial Vfinal atraso Tsubida Tdescida TVfinal Tpulso) V2 B gnd dc 5 * Carga varia de 0fF a 50fF CL out gnd CLOAD .PARAM CLOAD = 0ff .alter .PARAM CLOAD = 10ff .alter .PARAM CLOAD = 20ff .alter .PARAM CLOAD = 50ff Simulação no HSPICE Exemplo: nand2.cir (arquivo extraído do layout no L-Edit) * simulação transiente com passo de 0,1ns e duração de 0 a 200ns .tran 0.1N 200N .options post .measure tran tdr1 trig v(A) val=2.5 td=20ns rise=2 + targ v(out) val=2.5 fall=2 .measure tran tdf1 trig v(A) val=2.5 td=20ns fall=2 + targ v(out) val=2.5 rise=2 .measure tran tlh1 trig v(out) val=0.5 td=20ns rise=2 + targ v(out) val=4.5 rise=2 .measure tran thl1 trig v(out) val=4.5 td=20ns fall=2 + targ v(out) val=0.5 fall=2 * mede a potência no período da simulação em RMS .measure tot_power rms power .end
Baixar