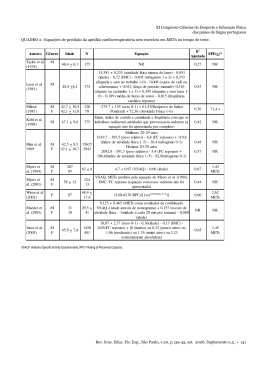
do-0161.pdf 1 de 1 http://www.medicinacomplementar.com.br/convertido/do-0161.htm Colesterol. Mio-inositol diminui o LDL colesterol em hiperlipêmicos com síndrome metabólica 01/11/2009 Lembremos que o inositol é um osmolito kosmotropo potente, isto é, ele funciona como forte estruturador da água citoplasmática: aumento das pontes de hidrogênio. Muitas doenças são produzidas por fatores que desestruturam a água citoplasmática, isto é, diminuem as pontes de hidrogênio. As pontes de hidrogênio são necessárias no intracelular para: 1- estabilizar a conformação das hélices do DNA e do RNA o que permite manter a estrutura da molécula e a sua característica especial do enrolar e desenrolar das hélices, 2- manter a estrutura tridimensional das enzimas e das proteínas, 3- estabilizar a estrutura terciária das enzimas e das proteínas, 4- manter a hidratação das proteínas, ácidos nucléicos e macromoléculas, 5- estabilizar, manter e proteger a membrana citoplasmática e mitocondrial, 6- interferir no potencial de membrana citoplasmático (Em) e no potencial de membrana mitocondrial (Delta-psi mt) 7- interferir na homeostasia dos poros da membrana citoplasmática, 8- interferir na velocidade das reações químicas intracelulares 9- participar das reações de hidrólise, 10- veicular informações, etc.... José de Felippe Junior Myo-inositol treatment increases serum plasmalogens and decreases small dense LDL, particularly in hyperlipidemic subjects with metabolic syndrome J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2008 Jun;54(3):196-202 Maeba R, Hara H, Ishikawa H, Hayashi S, Yoshimura N, Kusano J, Takeoka Y, Yasuda D, Okazaki T, Kinoshita M, Teramoto T. Department of Biochemistry, Teikyo University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. [email protected] BACKGROUND AND AIM: We have previously shown that serum plasmalogen levels positively correlate with HDL, and significantly decrease with aging, and may be related to LDL particle size. The objective of the present study was to investigate the effects of increased serum plasmalogens on lipidosis, particularly the appearance of atherogenic small dense LDL (sdLDL), of subjects with hyperlipidemia and metabolic syndrome (MetS). METHODS AND RESULTS: The effects of increased serum plasmalogen levels, induced by 2 wk of myo-inositol treatment, on several clinical and biochemical parameters were examined in 17 hyperlipidemic subjects including some with MetS. After myo-inositol treatment, significant increases in plasmalogen-related parameters, particularly ChoPlas, and significant decreases in atherogenic cholesterols including sdLDL, were observed. Among the hyperlipidemic subjects treated with myo-inositol, compared to subjects without MetS, subjects with MetS had a significant increase in plasmalogens and a tendency towards reduced sdLDL, high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), and blood glucose levels. Correlation analyses between the measured parameters showed that plasmalogens, as well as HDL, function as beneficial factors, and that sdLDL is a very important risk factor that shows positive correlations with many other risk factors. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that increased plasmalogen biosynthesis and/or serum levels are especially effective in improving MetS among hyperlipidemic subjects with MetS. Dose de mio inositol: 5g ao dia por 7 dias e depis 10 g ao dia 29/9/2011 17:11
Baixar