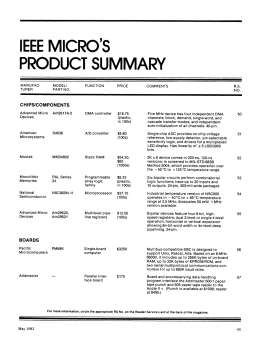
Unicode
ก๊กเฮงแซ่แต้
Игорь
Лукашев
徐順宏
Vladimir
Jelicačačić
Bjørn Vestergård
Adaptado por
Antonio Carlos Souza
Overview
• Não é filho do ASCII
– 8 bit characters
– ASCII
– O resto do mundo acordou pra o micro
• Unicode
– Atualmente na versão 6.0
– 107 mil caracteres
– Código dos caracteres
– Diferentes regiões
• Encoding and Decoding classes
• Example
The Good Old Days
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Foco na falta de acento, English letters
Cada letra, número, controle, etc
Representado por codes 0-127
Espaço, 32; “A”, 65; “a”, 97
Uso de 7 bits, 1 bit livre para muitos computers
Wordstar and the 8th bit
Below 32 – control bits 7, beep; 12, formfeed
8th bit, values 128-255
• Cada um tinha sua própria idéia
• IBM-PC -> graphics (horizontal bars,
vertical bars, bars with dangles, etc.)
• Outside U.S. different languages
– Code 130
8th bit, values 128-255
• Code pages – definição regional of bit values 128-255
– Israel: Code page 862
– Greek: Code page 737
– ISO/ANSI code pages
• Asia – Alphabets had thousands of characters
– No way to store in one byte (8 bits)
Unicode
• Not a 16-bit code
• A new way of thinking about characters
• Old way:
– Character “A” maps to memory or disk bits
– A-> 0100 0001
• Unicode way:
–
–
–
–
Each letter in every alphabet maps to a “code point”
Abstract concept
“A” is Platonic “form” – just floats out there
A -> U+0639 code point
Unicode
• Hello -> U+0048 U+0065 U+006C U+006C U+006F
• Storing in 2 bytes each:
– 0048 0065 006C 006C 006F (big endian)
– Or 4800 6500 6C00 6C00 6F00 (little endian)
• Necessário ter um Byte Order Mark (BOM) no início do
Stream
• UTF (Formato de Transformação Unicode, do inglês
Unicode Transformation Format)
• UCS (Conjunto Universal de Caracteres, do inglês
Universal Character Set)
Unicode
• Sistema de codificação UTF8
–
–
–
–
Stores Unicode points (magic numbers) as 8 bit bytes
Values 0-127 go into byte 1
Values 128+ go into bytes 2, 3, etc.
Caracter até 127, UTF8 é similar ao ASCII
• A UTF-7 é uma codificação não tão popular usada para
a codificação em 7 bits, e é normalmente considerada
obsoleta.
• Pode ser usada quando há restrições a caracteres com
o oitavo bit ligado; por exemplo, quando só se podem
usar caracteres ASCII válidos.
UNICODE Encodings
• UTF-8
• UTF-16 – characters stored in 2 byte, 16-bit
(halfword) sequences – also called UTF-2
• UTF-32 – characters stored in 4byte, 32 bit
sequences
• UTF-7 – forces a zero in high order bit - firewalls
• Ascii Encoding – everything above 7 bits is
dropped
Definitions
• .NET uses UTF-16 encoding internally to store
text
• Correio eletrônico - MIME
• Encoding:
– Transfere um conjunto de caracteres Unicode em
uma sequência de bytes
– Envia uma string para um arquivo ou stream de rede
• Decoding:
– Transfere uma sequencia de bytes em um conjunto
de Caracteres Unicode
– Lendo uma string de um arquivo ou network stream
• StreamReader, StreamWriter default to UTF-8
Encoding/Decoding Classes
• UTF32Encoding class
– Convert characters to and from UTF-32 encoding
• UnicodeEncoding class
– Convert characters to and from UTF-16 encoding
• UTF8Encoding class to convert to and from
UTF-8 encoding – 1, 2, 3, or 4 bytes per char
• ASCIIEncoding class to convert to and from
ASCII Encoding – drops all values > 127
• System.Text.Encoding supports a wide range
of ANSI/ISO encodings
Convert a string into a stream of
encoded bytes
1. Get an encoding object
Encoding e = Encoding.GetEncoding(“Korean”);
2. use the encoding object’s GetBytes() method to
convert a string into its byte representation
byte[ ] encoded;
encoded = e.GetBytes(“I’m gonna be Korean!”);
Demo: D:\_Framework 2.0 Training Kits\70-536\Chapter 03\EncodingDemo
Escrevendo um arquivo no
formato encoded
FileStream fs = new FileStream("text.txt", FileMode.OpenOrCreate);
...
StreamWriter t = new StreamWriter (fs, Encoding.UTF8); t.
Write("This is in UTF8");
Lendo um arquivo encoded
FileStream fs = new FileStream("text.txt", FileMode.Open);
...
StreamReader t = new StreamReader(fs, Encoding.UTF8);
String s = t.ReadLine();
Conclusão
• ASCII é um dos padrões mais velhos.
• UNICODE prove suporte multilingua.
• System.Text.Encoding tem métodos
estáticos para encoding and decoding
text.
• Use an overloaded Stream constructor
that accepts an encoding object when
writing a file.
• Not necessary to specify Encoding object
when reading, will default.
References
• www.unicode.org
• Unicode and .Net – what does .NET Provide?
http://www.developerfusion.co.uk/show/4710/3/
• Hello Unicode, Goodbye ASCII
http://www.nicecleanexample.com/ViewArticle.a
spx?TID=unicode_encoding
• The Absolute Minimum Every Software
Developer Absolutely, Positively Must Know
About Unicode and Character Sets (No
Excuses!)
http://www.joelonsoftware.com/articles/Unicode.
html
Baixar