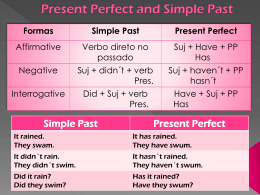
LÍNGUA INGLESA LÍNGUA INGLESA ASPECTO PERFECT ASPECTO PERFECT Professora Leila Eto Present Perfect Usamos o Present Perfect para uma ação no passado com um resultado agora. Formação have / has + Exemplos I’ve lost my key. (I can’t find my key now) We’ve bought g a new house. ((we have a new house now) George is on vacation. He has gone to London. past participle 1 O present perfect faz referência ao presente. Não usaremos o present perfect se não houver relação com o presente. Vejam j os exemplos: p Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone (e não has invented). Machado de Assis wrote many books (e não has written). Agora cuidado: I you we they he she it O present perfect é usado para ações que aconteceram em um tempo antes de agora. O tempo exato não é importante, com isso não usaremos expressões específicas de tempo como: yesterday one year ago last week when I was a child when I lived in Boston at that moment have + past participle has + past participle My father is a writer. He has written many books. Isso significa que ele ainda escreve livros. 2 Podemos usar expressões não específicas de tempo como: ever never once many times several times so far already yet I have never been to London. I have been to London twice. I think I have seen that TV program before. She has never traveled by plane. Principais usos de Present Perfect: 1. Experiência Podemos usar o Present Perfect p para indicar a experiência ou a falta de certa experiência. Exemplo I have been to London. 2. Mudança com o tempo You have grown since the last time I saw you. g has improved p since I moved to Myy Portuguese Brazil. A: Have you ever met him? B: No, I have not met him. 3 3. Realizações Usaremos o Present Perfect para listar realizações de indivíduos e da humanidade. Não se menciona o tempo especifico. Our daughter has learned how to read. Doctors have cured many deadly diseases. 5. Geralmente usamos o Present Perfect para anunciar um acontecimento recente. The road is closed. There has been an accident. 4. Uma ação incompleta que estamos esperando Geralmente usaremos o Present Perfect para expressarmos uma ação que era esperada e não ocorreu. Esse uso sugere que ainda estamos esperando a ação acontecer. It hasn’t stopped raining yet. George has still not arrived. Formação Forma Interrogativa Have I you we they Has he she it + past participle? 4 Infinitive begin break come do eat fly Short answers Yes, I have. No, I haven’t. Yes, she has. No, she hasn’t. Infinitive past simple past participle give go see ring speak write gave went saw rang spoke wrote given gone seen rung spoken written past simple began broke came did ate flew past participle begun broken come done eaten flown Usamos o Present Perfect com today/ this morning/ this evening quando tais períodos ainda não terminaram no momento da fala. I haven’t seen Diane this morning. 5 The first time + Present Perfect Diferença entre gone (to) e been (to) A expressão this is the first time … quando faz referência a um evento imediato é normalmente usada com present perfect. Patrick is always on vacation. He has gone to France. (ele está lá agora) Is this the first time you’ve flown on Air Canada? It’s the first time she has driven a car. EXERCÍCIOS DE FIXAÇÃO 1. Complete as frases com um verbo da lista. not / see go g forget g invite Are you going to the bank? No, I’ve already been to the bank. (já voltou) c. I know that man but I ____________________ his name. d. I’m looking for Mary. ______________ you ____________ her? a. Where’s Susan? She ________________out. b. Lauren is having a party tomorrow. She ___________________ a lot of people. 6 EXERCÍCIOS DE FIXAÇÃO Present perfect continuous 2. Use been ou gone. a. Carol isn’t here at the moment. She’s _____ to the post office. b. Robert has ________ out. He’ll be back in about an hour. c. I’ve just _________ to the supermarket. I bought lots of things. É usado para uma ação que finalizou ç no p passado e ainda recentemente ou começou prossegue no tempo. Formação Have / has + been + verb-ing It has been raining. (a rua ainda está molhada) I’ve been studying English for five years. (e ainda estudo) Usamos o present perfect continuous para perguntar ou dizer há quanto tempo alguma coisa está acontecendo. How long have you been reading that book? I’ve been working on the project for two weeks. She’s been talking on the phone for twenty minutes. 7 Forma interrogativa Have Has you been + verb-ing they been + verb-ing? we been + verb-ing Short answers: Yes, I have / No, I haven’t. Yes they have / No, Yes, No they haven haven’tt. Yes, she has / No, she hasn’t. she been + verb- ing? he been + verb- ing? it been + verb- ing? Vejamos a diferença: I’m studying French. (agora) y g French since August. g I’ve been studying How long have you been studying English? Uso de for / since Usamos for e since para expressarmos o tempo decorrido de determinado acontecimento. acontecimento For É usado para indicar período de tempo. 8 Exemplos I have known her for a long time. Louise has been learning Spanish for one year. year Não usamos for + all Usos comuns de for two days an hour a weekk five months ten years twenty minutes a long time Since É usado para indicar início de período. I’ve worked here all my life ( e não for all my life) Louise has been learning Spanish since 2010. 2010 I’ve lived in Miami since I was nine years old. 9 Usos comuns de since Wednesday 10 o o’clock clock May 1999 I arrived c. I’________________(read) a book _________ January. d. She ______________ (cook) ________ half an hour. EXERCÍCIOS DE FIXAÇÃO 1)Complete as frases com os verbos entre parênteses e use for/since a. Tom ______________________ (study English) ______ two hours. b. They __________________ (play soccer) _______ 4 o’clock . 2. Complete as frases usando for ou since. a. My sister has lived in Montreal _____________ five years. b. They have been in Ottawa _____________ 1994. 10 just / already / yet c. She has been married _______________ December. d. He has studied History ________________ a long time. Just Significa pouco tempo atrás. Is Bob here? No, he’s just gone. (he has just gone) Already Are you hungry? No, I’ve just had lunch. Significa antes do esperado. Don’t forget to send the email, will you? I’ve already sent it. 11 Yet Significa até agora. Have Karen and Phil arrived yet? No, not yet. É usado em frases negativas e interrogativas. Geralmente aparece ao final da frase. Have you made the phone calls? No, I haven’t made them yet. Are Karen and Phil here? No, they haven’t arrived yet. Has Richard started a new job yet? No, he starts next week. EXERCICÍOS DE FIXAÇÃO 1. Complete as frases. Use already + present perfect. c. Do you want to call her?__________________ _______________________________________ d. When does your sister start a new job?______ _______________________________________ a. What time is Ann leaving? _________________ ________________________________________ b. Don’t forget to invite Sue. __________________ ________________________________________ 12 2. Escreva frases usando yet. a. ________________________________? (Karen and Phil / arrive) y No, not yet. ever / never Ever Have you ever been to New York? (In your life) Yes, once. b. Have you done your homework? __________________________________ (I / do) Never I’ve never played hockey. Ever = já (alguma vez) EXERCÍCIOS DE FIXAÇÃO Have you ever been to China? Yes, once. 1. Have you ever played hockey? No, never. a. (you / ever / climb/ mountain?) ______________________________________ b. (you / ever / be / London?) ______________________________________ Faça perguntas parênteses: p com as palavras entre 13 ago c. (you / ever/ eat / caviar?) ______________________________________ d. (you / ever / speak / famous person?) ______________________________________ Ago = antes de agora É usado com passado. Jennifer started a new course three days ago. I had lunch twenty minutes ago. Vejam a diferença entre ago e for: Susan and Dennis got married 10 years ago. Susan S and d Dennis D i have h b been married i d for f t ten years. Ago e for When did Lauren arrive in Montreal? She arrived in Montreal five days ago. How long has she been in Los Angeles? She has been to Los Angeles for two days. 14 EXERCÍCIOS DE FIXAÇÃO 1. Complete as frases com as palavras entre parênteses + ago ou for. c. I bought this CD _________________ (a few days). d. Flo has been studying English ______________ ((five yyears). ) a. They have been married _________________ (ten years). b. They got married _________________ (ten years). Past Perfect Enquanto o present perfect refere-se a um tempo até o momento, o past perfect refere-se a um tempo até um momento no passado. Estudemos: Há uma semana: At 9:30: Paul went to the party but he didn’t see Mary. He went home at 11:00 and Mary arrived at the party at 11:30. When Mary arrived at the party, Paul had left. 15 Vejamos a linha do tempo: A B C hoje uma semana atrás A: Paul went to the party at 9:30. B: He went home at 11:00. C: Mary arrived at 11:30. When Mary arrived at the party, Paul had left. When I arrived home, my parents had already left. (Primeira ação: meus pais partiram. Segunda ação: eu cheguei em casa). Formação Had + past participle Com isso diremos que: O past perfect é usado quando duas ações ocorreram no passado. Para a primeira ação (no tempo) utilizaremos o past perfect e para a segunda o simple past. EXERCÍCIOS DE FIXAÇÃO 1. Coloque o verbo no tempo verbal correto, past perfect ou simple past. a. I was very tired when I got home, so I _____________________ (go) straight to bed. b. The house was quiet when I arrived. Everybody _______________________ (go) to bed. 16 Past Perfect Continuous c. When Jane finished her homework, Joe _______________________ (leave) for work. Formação had been + verb -ing ing Exemplos: He had been waiting there for more than two hours when she finally arrived. Forma interrogativa Had he been waiting there for more than two hours when she finally arrived? Forma negativa He had not been waiting there for more than two hours when she finally arrived Principais usos 1. Duração de tempo antes de alguma coisa no passado passado X presente futuro They had been talking for two hours before Helen arrived. 17 2. Causa de algo no passado Richard was tired because he had been playing tennis. Past continuous x past perfect O Past Continuous enfatiza ações que são interrompidas e o Past Perfect Continuous enfatiza uma duração de tempo antes de algo no passado. He was tired because he was working hard. He was tired because he had been working hard. Will have done (future perfect) 2. Também demonstra que algo acontecerá antes de determinado tempo no futuro. past p participle p p para dizer 1. Usamos will have + p que algo acontecerá antes de outra ação no futuro. We’re late. The p party y will have started byy the time we arrive. 18 Outro uso de will have + past participle: By next July, I will have received my promotion. I am not going to have finished this lesson by 2 o'clock. Paul and Sharon have been married for 9 years. Next year they will have been married for 10 years EXERCÍCIOS DE FIXAÇÃO 1. Complete as frases com will be –ing ou will have + past participle. a. Don’t call me between 8 and 9. I _________________ (watch) the soap opera. b. Call me after 9 o´clock. I _____________________(finish) dinner then. c) This time next week I ___________________ (swim) in the sea. d) I’m going to study French from 5 o’ clock until 6 o’clock. At 5:30 I ___________________ (study) French. e) Ann goes to school at 7:00 a.m, so she won’t be at home at 9:00 a.m. She____________________ (go) to school. 19 GABARITO GABARITO Present Perfect Present Perfect 1. a. has gone b. has invited c. have forgotten d. Haven’t / seen 2. a. gone b. gone c. been GABARITO Present perfect continuous / for / since 1. a. has been studying English for b. have been playing soccer since c. ‘ve been reading a book since d. has been cooking for GABARITO Ever / never / for / since 2. a. for b. since c. since d. for 20 GABARITO already 1. a. Ann has already left. b. I have already invited her. c. I have already called her. d. She has already started it. GABARITO Ever / never a. Have yyou ever climbed a mountain? b. Have you ever been to London? c. Have you ever eaten caviar? d. Have you ever spoken to a famous person? GABARITO yet 2. a. Have Karen and Phil arrived yet? b. I haven’t done my homework yet. GABARITO Ago 1. a. for ten years b. ten years ago c. a few days ago d. for five years 21 GABARITO Past perfect 1. a. went b. had gone c. had left GABARITO Future perfect a. will be watching b. will have finished c. will be swimming d. will be studying e. will have gone 22
Baixar