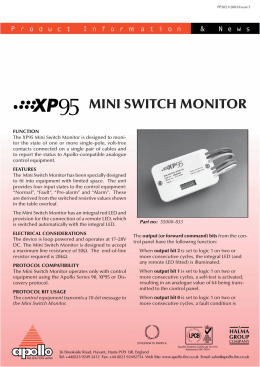
Código de Huffman Código de Huffman Código aritmético Run-Length Encoding (RLE) Codificação preditiva • Predictive Coding transmit the difference between estimate of future sample & the sample itself. - Delta modulation - DPCM - Adaptive predictive coding - Differential frame coding Differential Pulse Code Modulation (DPCM) Delta Modulation (t) x(t) + - y (t) f (t) Delta modulation y(t) x(t) f(t) t Codificação de planos de bit abcdef a b c d e f Codificação por transformação • Transform Coding - transform image - code the coefficients of the transform - transmit them - reconstruct by inverse transform • Benefits - transform coeff. relatively uncorrelated - energy is highly compacted - reasonable robust relative to channel errors Padrão JPEG "Joint Photographic Expert Group". Voted as international standard in 1992. Works with color and grayscale images, e.g., satellite, medical, ... Lossy and lossless JPEG (intraframe) First generation JPEG uses DCT+Run length Huffman entropy coding. Second generation JPEG (JPEG2000) uses wavelet transform + bit plane coding + Arithmetic entropy coding. Visão geral JPEG DCT (Discrete Cosine Transformation) Quantization zigzag Scan DPCM on DC component RLE on AC Components Entropy Coding Porquê DCT e não DFT • DCT is similar to DFT, but can provide a better approximation with fewer coefficients • The coefficients of DCT are real valued instead of complex valued in DFT. • DCT reduces Gibbs effect between subimage boundaries. Porquê DCT e não DFT DCT Transformada discreta de cosseno Inversa: Funções base DCT de 8x8 • Each 8x8 block can be looked at as a weighted sum of these basis functions. • The process of 2D DCT is also the process of finding those weights. DCT Quantização F'[u, v] = round ( F[u, v] / q[u, v] ). Why? -- To reduce number of bits per sample Example: 101101 = 45 (6 bits). q[u, v] = 4 --> Truncate to 4 bits: 1011 = 11. Quantization error is the main source of the Lossy Compression. Tabelas de quantização Luminância Cromaticidades Um fator de qualidade multiplica a matriz de quantização. Varredura Zig-Zag Why? -- To group low frequency coefficients in top of vector. Maps 8 x 8 to a 1 x 64 vector. Codifica DC com DPCM DC component is large and varied, but often close to previous value. Encode the difference from previous 8 x 8 blocks -- DPCM Codifica AC com RLE 1 x 64 vector has lots of zeros in it Keeps skip and value, where skip is the number of zeros and value is the next non-zero component. Send (0,0) as end-of-block sentinel value. Codificação entrópica Categorize DC values into SIZE (number of bits needed to represent) and actual bits. Example: if DC value is 4, 3 bits are needed. Send off SIZE as Huffman symbol, followed by actual 3 bits. For AC components two symbols are used: Symbol_1: (skip, SIZE), Symbol_2: actual bits. Symbol_1 (skip, SIZE) is encoded using the Huffman coding, Symbol_2 is not encoded. Huffman Tables can be custom (sent in header) or default. Categorias de codificação Size Amplitude -1.1 2 -3..-2,2..3 3 -7..-4,4..7 4 -15..-8,8..15 5 -31..-16,16..31 6 -63..-32,32..63 7 -127..-64,64..127 8 -255..-128,128..255 9 -511..-256,256..511 10 -1023..512,512..1023 Código de luminância Categoria Tamanho Code 0 5 00 1 3 010 2 4 011 3 5 100 4 7 101 5 8 110 6 10 1110 7 12 11110 8 14 111110 9 16 1111110 10 18 11111110 11 20 111111110 Exemplo JPEG 2000 Exemplos Original Exemplos JPEG 27:1 Exemplos JPEG2000 27:1
Baixar