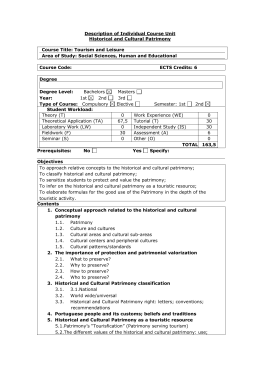
Course Plan Code of the course: M115 Study Cycle: 2nd CYCLE, 120 ECTS Negotiation and Leadership MASTER IN MARKETING MANAGEMENT Year: 1st Semester: 1st ECTS credits: 6 Code: M100 Field of Study: Social Sciences and Humanities Academic year: 2013-2014 Lecturer: Paula Campos Language of instruction: Portuguese / English Type and number of contact hours: Working hours (total): L TP LP FW S 9 13 10 9 2 I T 2 O Total 45 L - Lectures, TP - Theoretical-practical, LP - Laboratory Practices, FW Field Work, S - Seminar I - Internship, T - Tutorial, O - Other Learning outcomes of the curricular unit: From a global perspective is expected that the student contextualize Leadership and Negotiation in the current social, political, economic context, developing skills of observation, analysis and intervention in organizational contexts through the elaboration of an organizational leader profile. Comparing it with the leadership approaches in the literature reviewed, it is also expected that the student is able to develop leadership skills either in himself or in other employees Syllabus: 1. Leadership, globalization and the competitive environment 1.1. Lead in relation to the external environment 1.2. Lead in relation to the internal environment 2. Theories and models of leadership 2.1. Classical and current approaches leadership 2.2. Models of leadership 3. Negotiation 3.1. Structure of business processes 3.2. Planning for negotiation: strategies and tactics 3.3. Negotiation techniques 3.4. Leadership in the cognitive and cultural contexts 3.5. Negotiation and mediation Demonstration of the syllabus coherence with the curricular unit's objectives: When planning the Course, a model was structured, required before the beginning of the semester, which must include the Course goals and syllabus, so the coherence between the course goals and its implementation can be analysed through the syllabus to teach. These plans are reviewed by the scientific tutor of the area where the Course is integrated as well as by the course director, with a thorough discussion with the course’s responsible teacher, before its validation by the Science Council. Teaching methodologies (including evaluation): The SIM methodology includes classroom training, blended learning training and market training thus ensuring the scientific training of students, their ability to do research and collect information and their adaptation to a constantly changing market. In this Course, the syllabuses developed were applied to an interdisciplinary study created with the collaboration of a company thus ensuring compliance with the goals set. Students may enroll in one of three assessment methods: ongoing, regular, and final assessment. With different implications in terms of mandatory attendance in classes and types of work to do. Continuous assessment involves three points divided between 50% group work and 50% individual work. In this Course, an ongoing assessment is done by writing two reports together with another student and one individual test. Regular assessment involves only two evaluations and in the final assessment only one evaluation is carried out at the end of the semester 1 Course Plan Demonstration of the coherence between the teaching methodologies and the learning outcomes: In terms of teaching methodologies, we consider it essential to highlight the basic assumptions underlying the approach advocated by IPAM. In fact, we consider it to be essential that the teacher assumes the role of tutor and facilitator of the learning experience by using active and participative methodologies which support the construction of knowledge while interacting with the environment. Within this particular context the SIM Method (Classroom, Internet and Market) implies that the teacher has to describe all the details while planning the activities to be undertaken in the three environments: classroom, internet, and market. This detailed planning is integrated into the Course plan which is validated as previously mentioned. Therefore, before the beginning of the semester, each teacher has to present the methodologies which they intend to use, relating them with the course goals, as well as with the results/competences to develop. Main Bibliography: - Boyatzis, R.; Goleman, D.; McKee, A. (2008) Os novos líderes: a inteligência emocional nas organizações, Lisboa, Gradiva Fisher, R.; Ertel, D. (2008) Como conduzir uma negociação, Lisboa, Lua de Papel. - BYHAM, William C. - Formando líderes : como identificar, desenvolver e reter talentos de liderança. São Paulo: Prentice Hall , 2003. - Alan - Liderança inteligente: criar a paixão pela mudança. 4.ª ed. Lisboa : Actual Editora, 2006. - REGO, Arménio - Liderança positiva. 1ª ed. Lisboa: Sílabo , 2009. - BLANCHARD, Ken - Um Nível Superior de Liderança : com sócios e consultores das empresas de Ken Blanchard. Lisboa : Actual Editora , 2007. - FISHER, Roger - Como conduzir uma negociação: chegar a acordo sem ceder. 8ª ed.. : AsaPorto : Lua de papel, 2008. - GESTOSO, Carlos Guillén - Estratégias de negociação. Mangualde : Edições Pedago , 2007. - SIMÕES, Eduardo - Negociação nas organizações : contextos sociais e processos psicológicos. Lisboa : Editora RH , 2008. 2
Download