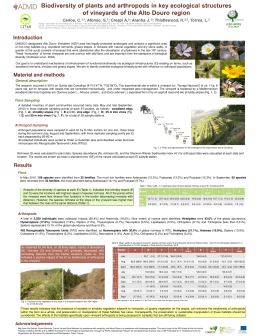
Monitoring arthropod diversity in Douro Wine Region vineyards Alexis Rataux, Cristina Carlos, Fátima Gonçalves, José Aranha, Josépha Guenser, Fernando Alves, Maarten Van Helden Why the interest about Biodiversity in DWR? Ex. Quinta das Carvalhas 20% scrubland (42% of the surface with scrubland) • Growers researchers are concerned in understanding they Alto Douroand Vinhateiro (ADV) – 10% of the Douro Winehow Region couldHa improve the presence of natural enemies in cultivated landscapes 24960 250 000 ha 13% olive groves • IOBC guidelines: the presence of Ecological Compensation Areas (ECA) must cover at least 5 % of the total farm surface (excluding 39% vineyards forest) • UNESCO designated Alto Douro Vinhateiro (ADV) area has legally protected landscapes and contains a significant area of non-crop habitats (e.g. woodland remnants, grassy slopes, or terraces with natural vegetation and dry stone walls). BIODIVINE – main goals • To understand the impact of the lanscape on biodiversity (in particular of some semi-natural elements left in the countryside such as hedges, groves, scrubland) • To understand how the presence of those elements nearby the vineyards can enhance the presence of arthropods? 1- Scrubland Material & methods 2- Vineyard • Characterization of the landscape by GIS 5 different classes of land use (5 habitats), replicated 5 times 3- Olive groves, 4- olives hedges 5- Urban Experimental Sites • 25 points monitorized in 5 pilot farms (500 ha) located in the ADV area (S. Luíz, Seixo/Bateiras, Carvalhas & Ventozelo) Material 2 types of&Traps methods in each point (5 / habitat) 10 weeks of assessment (April-June) Combi trap Pitfall trap Classification of arthropods by RBA method Results Buffer’s radius (m) Habitats (%): Dirt roads Olive hedges Olive groves Riparian forest River Sealed roads Scrubland Urban sites Vineyards 50 6,66 1,58 15,53 1,81 0,30 2,62 23,80 6,97 39,13 100 6,48 1,21 10,42 1,36 2,01 2,07 25,85 4,90 44,03 Buffer’s radius (m) Global surface (ha) Interstitial space (ha) Interstitial space (%) Shannon W. Index for landscape 50 0,59 0,01 2% 0,64 150 6,35 1,09 8,15 1,06 3,33 1,74 24,87 2,70 49,07 200 5,88 0,95 6,38 0,96 4,61 1,44 23,13 1,92 53,19 100 150 200 2,36 5,32 9,47 0,04 0,09 0,15 2% 2% 2% 0,87 0,97 1,01 Impact of the lanscape in some natural enemies Ripys. Scrub Olive hedge vines Urban Olive groves Shannon W. Index Spiders /- / - / - - --- Coccinellidae / /- / / ++ -+- + ++ + ++ Staphylinid / /- / /- / ++ ++ + + ++ Opilion / / / / / + / / - non sign.; + - sig. (0,05); ++ - sig. (0,01); Results 52187 indiv. , 27 orders identified, 5 classes of Arthropoda Abundance % Richness % Total 52187 - 789 - Combi 46859 89,7 703 89,1 Pitfall 5328 10,2 316 40,1 Abundance Others 13% Hymenopte ra 15% Diptera 20% 90% Richness Others Araneae 3% 3% Hemiptera 13% 10% Coleoptera 46% Araneae 8% Coleoptera 25% Hymenopter a 22% Hemiptera 19% Diptera 13% Analysis of Order by habitat Combi trap 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Coleoptera, Diptera, Hemiptera Hymenoptera, Spiders Olive hedges Urban sites Coleoptera Hemiptera Scrubland Olive groves 100% Hymenoptera Araneae Diptera Lepidoptera Others Pitfall trap Vineyard 80% 60% Order distribution were different among habitats for both Combi- and Pitfall traps 40% 20% 0% Olive hedges Urban sites Coleoptera Centipeda Hemiptera Opilion Vineyard Scrubland Olive groves Hymenoptera Others Araneae Impact of the habitat on the abundance Abundance Combi Olive Hedges 7523 Scrubland 12846 Urban 10893 Olive groves 7991 Vineyard 7606 46859 Habitat Abundance Pitfall 1135 756 1114 931 1392 5328 % 16,1 27,4 23,2 17,1 16,2 % 21,3 14,2 20,9 17,5 26,1 Global Abundance 8658 13602 12007 8922 8998 52187 % 16,6 26,1 23,0 17,1 17,2 a Scrubland habitat attracted more indiv. than vineyard or olive hedges ab bc Scrubland Urban c c Olive groves Vineyard Olive hedges Impact of the habitat on Richness Richness / habitat 100% 90% a 80% ab 70% abc 68% 60% 60% 64% 67% bc 63% a 50% c a 40% a a a 30% ab bc bc 20% c 10% a ab bc b c bc 0% haie: 473 urbain: 536 vigne: 507 maquis: 527 verger: 494 Olive groves Olive hedges Urban Vines Scrubland For arthropods’ richness, the statistical tests did not show any significant differences. The impact of the habitat in each order must be analyzed separately Discussion – 1st year data • The impact that scrubland and olive groves could have on biodiversity around vineyards and in particular in some orders and families of Arthropoda Thank you for your atention!
Baixar